The male pelvic floor is a frequently overlooked area, yet it plays a vital role in several important bodily functions. From continence to sexual health and postural stability, this group of muscles is central to men’s well-being. In this article, we’ll explore what the male pelvic floor is, how it works, and what issues can arise.
What Is the Male Pelvic Floor?
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues located at the base of the pelvis, between the pubic bone at the front and the tailbone (coccyx) at the back. In men, it forms a muscular hammock that supports several pelvic organs, including the bladder, prostate, rectum, and external genitalia.
Detailed Anatomy
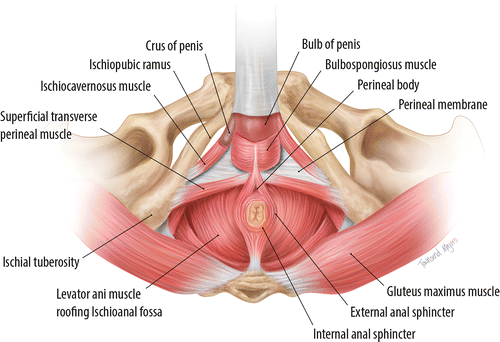
The pelvic floor includes several key muscles:
Pubococcygeus muscle: part of the levator ani muscle group, supports the rectum.
Transverse perineal muscle: contributes to pelvic support.
External anal sphincter: controls anal continence.
Bulbospongiosus muscle: important for erection and ejaculation.
Ischiocavernosus muscle: helps maintain erection.
What Are the Functions of the Male Pelvic Floor?
The male pelvic floor serves several essential functions:
Maintaining urinary and fecal continence by controlling sphincter openings.
Sexual function, including erection, ejaculation, and sexual pleasure.
Supporting pelvic organs to prevent prolapse (organ descent).
Stability and posture, as part of the pelvic girdle that stabilizes the pelvis and trunk.
What Problems Can Affect the Male Pelvic Floor?
The pelvic floor can be affected by various conditions, often poorly understood or taboo:
1. Urinary and fecal incontinence
Muscle or nerve weakness can cause leakage of urine or feces, especially after prostate surgery, trauma, or aging.

2. Erectile dysfunction and ejaculation problems
The pelvic floor plays a role in erection and ejaculation; muscular or neurological issues can lead to sexual difficulties.
3. Chronic perineal pain
Certain conditions or muscle tension can cause persistent pain in the pelvic area, affecting daily life.
4. Problems related to increased abdominal pressure
Chronic constipation, repetitive straining, or certain sports can fatigue the pelvic floor and cause disorders.
How to Maintain a Healthy Pelvic Floor?
The pelvic floor can be strengthened and rehabilitated through specific exercises, commonly known as Kegel exercises. These involve voluntary contractions of the pelvic muscles and can be supported by techniques like biofeedback or electrical stimulation. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including weight management, balanced diet, and regular physical activity, also contributes to pelvic health.

When to Consult a Specialist?
If you experience symptoms such as urinary leakage, pelvic pain, sexual difficulties, or a feeling of pelvic heaviness, it is important to consult a healthcare professional (physiotherapist, urologist, etc.) for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.
Our specialised physiotherapists are here to help you—get in touch to learn more.