Post Natal :
What can happen after your pregnancy ?
Post Natal :
What can happen after your pregnancy ?

Post natal check up
Description
2 sessions:
- Women Health for check of abdominal and pelvis muscle, c section, episiotomy , incontinence…
- Check of abdominal area: check of diastasis (gap between rectus abdominus)
- Check of good automatism when couging, running,… (most of the time, after a pregnancy your transverse muscle is weaker than before leading to a lack of abdominal control. This weakness is one of the reason of pelvic pain, incontinence, urgency…
- Check of c-section scar and teaching auto massage
- Check of episiotomy or tear scar and teachinh massage
- Check of strenght, endurance and functions of pelvic floor
- Osteopathy for movement and position of hip and pelvis bone, abdominal organ and diaphragm and breathing
Stress incontinence
Description
Both pregnancy and labour traumatised the pelvi-perineo-urinary system. Multiple injuries and dysfunctions can occur. They are named vesical instability: 13 to 26% of women suffer from urinary problem after giving birth. It can manifest as:
- Dysuria with post-micturition residue: Dysuria is characterised by a difficulty to empty the bladder, with or without associated pain. This dysfunction is commonly overlooked because painless and with a progressive apparition. Dysuria is often associated with urine leakage when standing up afterward.

- Urgency micturition is a sudden irrepressible urge to urinate
- Urinary incontinence by urgency is an involuntary urine leakage preceded by compelling urge to urinate, leading sometimes to complete urination. This type of incontinence is caused by an involuntary contraction of the bladder and it is not link to physical activity. It is named instable bladder or hyperactive bladder. It can appear in certain situation associated with reflex micturition such as incontrollable laugh, fear, orgasm…
- Effort urinary incontinence: 30% to 50% of women suffer from this condition. Risk increase with number of pregnancy and age. It is characterized by urine leakage (not preceded by urgency) occurring when sneezing, laughing, coughing, and lifting or during physical activities (running, jumping…). In extreme cases, even walking can trigger it. This type of incontinence is due to a brutal abdominal pressure increase causing leaking through either hypermobility of the urethral canal (urinary canal) or sphincter failure (weakness of muscles blocking the urethra).
- Mixt urinary incontinence is a combination of two above dysfunctions

Anal Incontinence
Description
Anal continence is a complex mechanism: As we eat, food is digested by our stomach then by our intestine to reach the last part named rectum. Two sphincters close the rectum: an internal one with an involuntary control and an external one with a voluntary control. As the stools arrive in the rectum, it distends the wall which is supposed to trigger the need to go to the loo. When it is not possible to go, a voluntary contraction, of the external sphincter and of another pelvis muscle named pubo rectal muscle, diminishes the need. After a while, the internal sphincter also contract but involuntary, allowing us not be forced to voluntary contract the external sphincter all the time without having to rush to the loo. When the external sphincter or other pelvis muscles are teared, the voluntary contraction is not possible anymore. Consequently, the time between the stools entering the rectum and having to exit is drastically shortened, we speak of anal incontinence. Rectum works as a tank collecting stool allowing a delayed elimination. However, if the rectal compliance is reduced, this tank is smaller and can’t conserve the stools compiling to eliminate them more frequently. On the opposite, if the rectal compliance is increased or if the rectal sensibility is impaired, stools will accumulate leading to anal incontinence by overflow. Rectum static dysfunctions are often the source of anal incontinence. For exteriorised prolapse (in very long labour or following use of forceps) anal incontinence is also frequent.
Pregnancy Gym Classes
2nd and 4th wednesday of the month-
At 6:00 PM
-
Kentish Town practice
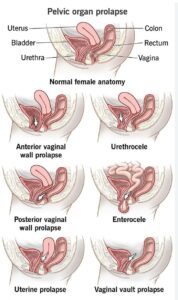
Prolapsus
One woman out of 3 over 50 years old has a prolapse, often minor and symptomless. However, prolapses worsen and become symptomatic, especially pass 60 years old. Women describe a vaginal ball, a sensation of something going down or/and of heaviness. What is a prolapse? How is it defined? We speak about genital-urinary prolapse when there is a temporary or permanent lowering of one or more pelvic organs. They will push and deform the vaginal wall, creating a bump on the perineum or even exiting through the vagina. These pelvic organs are:
- Bladder: named cystocele
- Uterus: named hysterocele
- More rarely Rectum: named rectocele
C’section
Description
After surgery abdominal surgery (C-section, appendectomy…), the surgeon cut through different layer of muscles, fascia and organ. Thanks to the scaring process, these layers will close completely. Unfortunately, it also create new link between these layers called adhesions. These adhesions are problematic as they prevent movement and the normal function of the different tissue. For example, an adhesion between muscular tissue and organ will diminish the contraction of the muscle and may trigger pain.

Diastasis
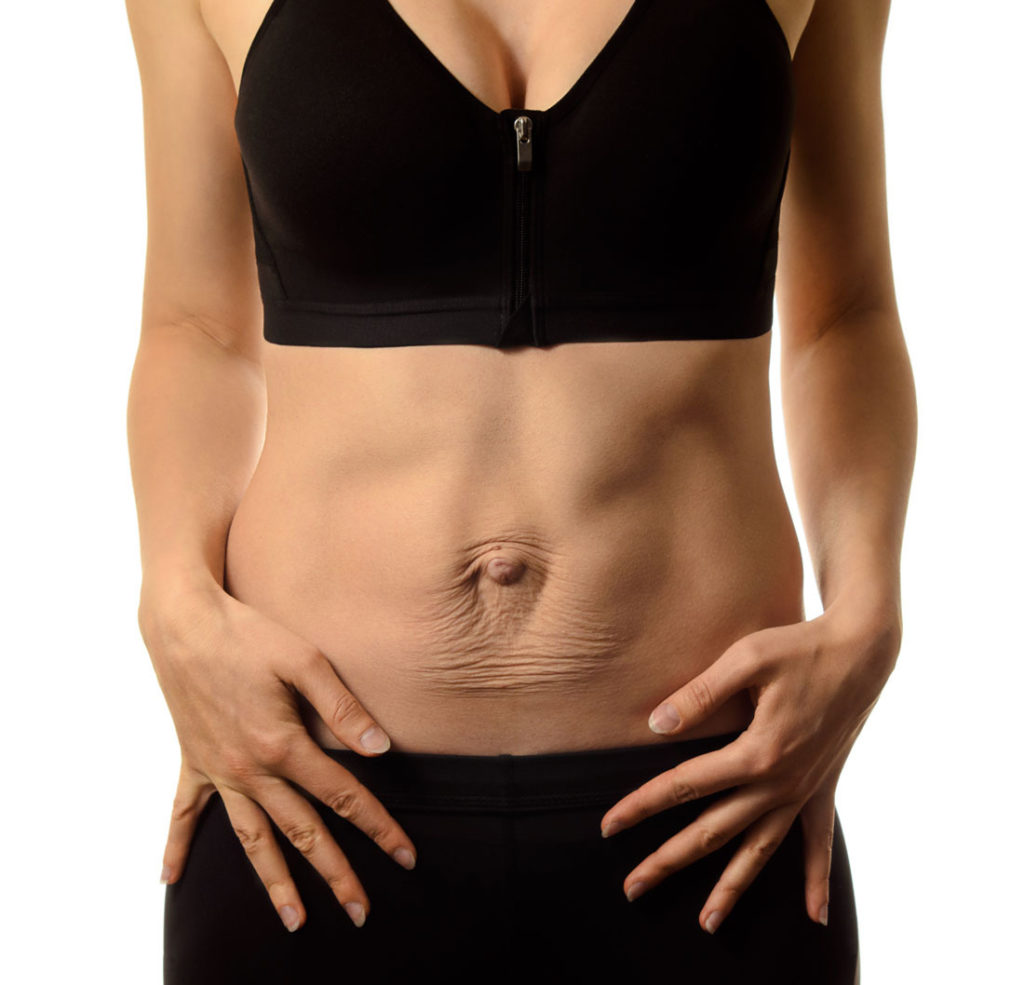
Description
A large variety of pain can appear after delivery, your whole body having suffer a massive trauma throughout the pregnancy and labour.
- Ano-rectal pain, often link to difficulty to eliminate stools, require bowel habits and postural education
- Sacral, coccyx (tailbone) and thoraco-lombar-abdominal-pelvi-perineum pains result from postural and biomechanical change occurring over the pregnancy: shoulder inside, increased lordosis (lower back arch backward), abdomen shift forward, hips in external rotation (feet outside like a cowboy)
- Pain related to pudendal nerve: it is characterized by a perineal pain often on one side, similar as a burning sensation with sometimes pain inside the anus. These symptoms are aggravated in sitting position and relived in standing/lying position. It can also be associated to a pain around vaginal orifice
- Pain due to episiotomy scar or suture break, increased in sitting position and during sexual intercourse
- Pain at external anal sphincter level, due to injury, tear, large episiotomy. It presents as an intense and punctual pain trigger by bowel movement and sometimes in sitting position
- Abdominal pain: C-section scar are one of the cause but rectus addomini diastasis lead to dysfunction of abdominal muscles and may result in pain while performing simple movement and task of life.
Constipation
Constipation
Description
It is well known pregnant women and new mom are constipated (you can find on our YouTube channel and blog various video/articles on the causes and how to prevent it) (link) There are several causes:
- Pregnancy hormonal changes slow down bowel activity creating constipation within the intestine.
- After giving birth, C-section scar, tear and episiotomy make it extremely painful to have a bowel movement. In this case, we speak about terminal constipation.
- Furthermore, pressure creating during labour lead to haemorrhoid and consequently painful bowel movement an again a terminal constipation.
- Finally, growing uterus push rectum backward creating an angle with the anus compromising stool expulsion.

Blood circulation issues/Celuliti
Description
 Thanks (not really) to your hormones, diameter of you veins increase. Furthermore, a new venous system develops for your baby and the weight of your growing baby press on the biggest vein of your body the vena cava. The combination of these 3 elements prevents the blood to come back normally from your lower limbs to your legs, creating sensation of heavy legs, welling and varices. On a long term, it also causes cellulite.
Thanks (not really) to your hormones, diameter of you veins increase. Furthermore, a new venous system develops for your baby and the weight of your growing baby press on the biggest vein of your body the vena cava. The combination of these 3 elements prevents the blood to come back normally from your lower limbs to your legs, creating sensation of heavy legs, welling and varices. On a long term, it also causes cellulite.
NB: this reduce blood return can also cause dizziness in pregnant women when lying on your back.
Treatments
For more informations, or to book a session, feel free to contact us: